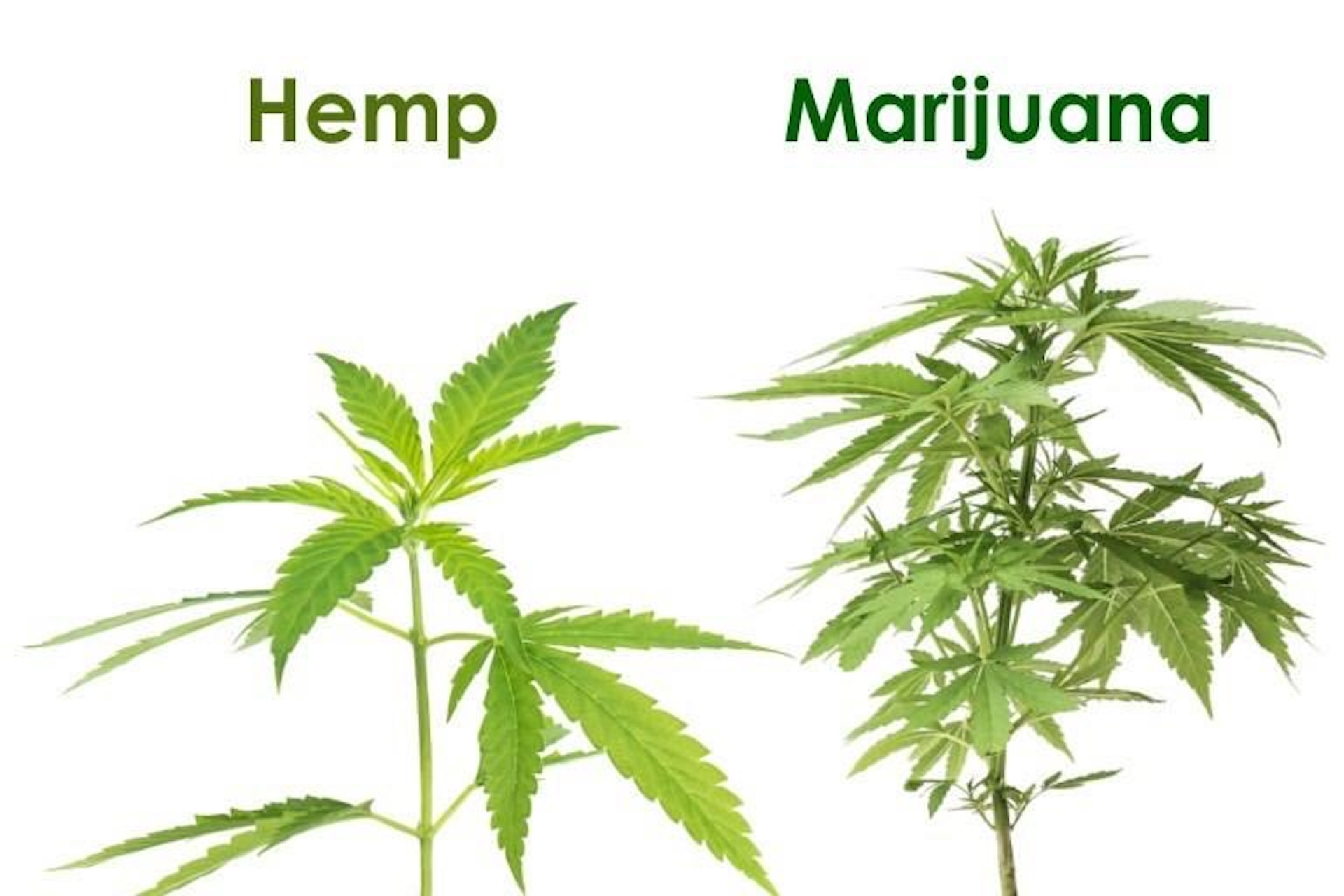
Hemp boasts a rich history and was among the earliest cultivated plants, its roots dating back 6,000 years ago in ancient Mesopotamia and China. This versatile plant found diverse uses, from textiles to food and medicines. Below you will find a few key important references on Hemp Plant History:
- 6,000 BCE: Hemp is one of the first plants cultivated for textiles in ancient Mesopotamia.
- 2,700 BCE: The Chinese began using Hemp for textiles, paper, and medicines.
- 1,500 BCE: Hemp cultivation spreads to the Indian subcontinent.
- 500 BCE: Hemp cultivation becomes common in Europe.
- 15th Century: Hemp sails and ropes are used on Christopher Columbus’ ships.
- 17th Century: Hemp farming is encouraged in the American colonies.
- 18th Century: The Declaration of Independence is drafted on Hemp paper.
- 20th Century: Hemp faces restrictions and regulations in the United States and other countries.
- 1937 AD: The U.S. Marijuana Tax Act restricts all Hemp production.
- 2016 AD: The U.S. Farm Bill legalizes Hemp cultivation, differentiating it from marijuana with THC.
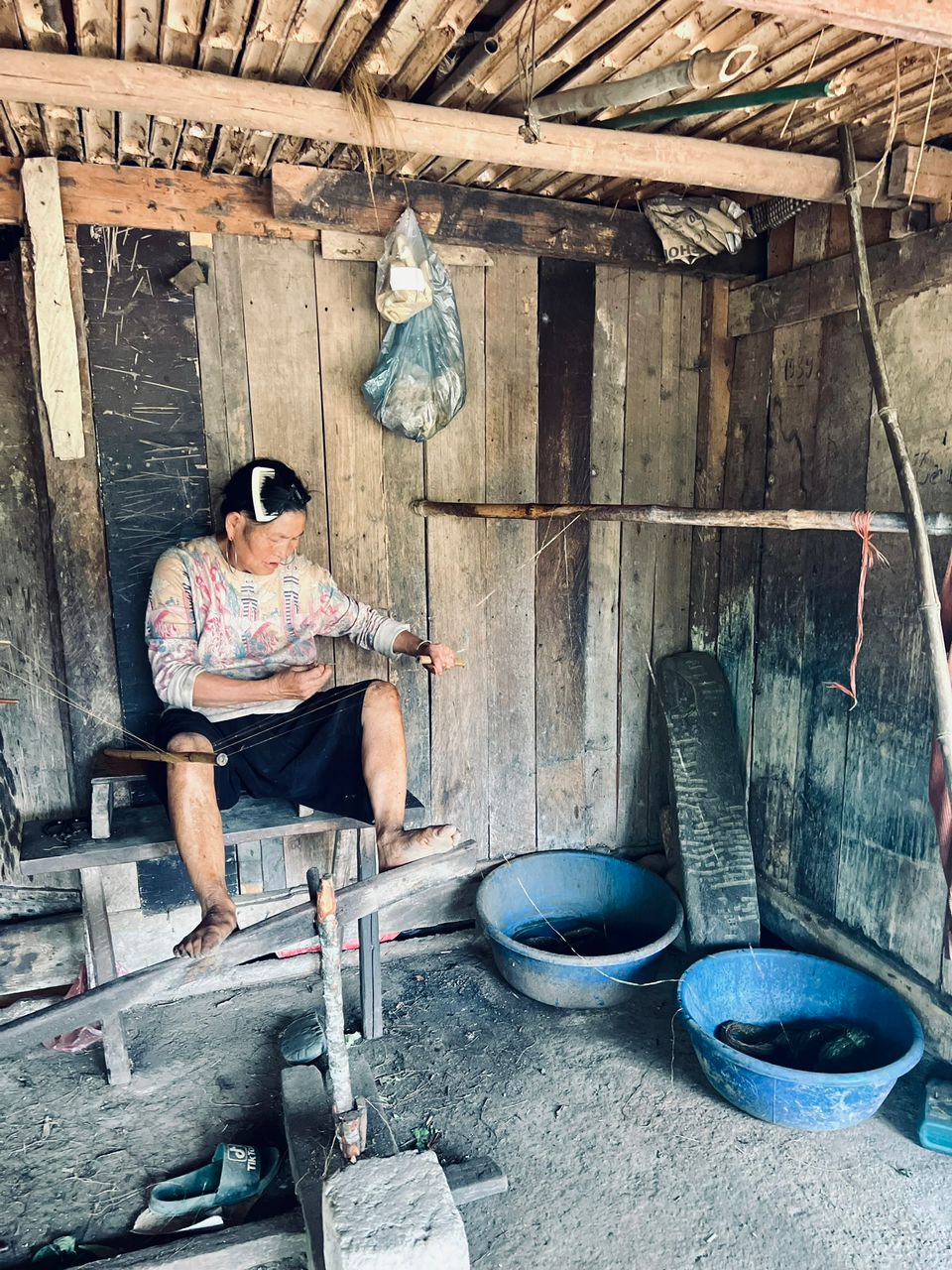

Time honored tradition of fiber weaving and still in practice inside Vietnam today
The Difference
Hemp fiber plants and ornamental hemp plants differ significantly in various aspects of their growth, use and characteristics. Hemp fiber plants are taller, with a height of 6 to 8 feet at maturity and have a 12 to 14 week growing period.
They produce a substantial number of seeds in their flowers, primarily cultivated for its fiber production, yielding around 3 to 4 tons of fiber per acre and 500 pounds of grain.
In contrast, ornamental hemp plants are shorter, reaching 4 to 6 feet at maturity, and have a slightly shorter growing period of 10 to 14 weeks. They are typically feminized, containing minimal to no seeds, and are primarily grown for their higher oil yield, with 1 liter of oil extracted from every 2,500 pounds of biomass. Ornamental hemp yields an average of 8,000 pounds of biomass per acre. The difference makes each type of hemp suitable for distinct purposes and appropriate cultivation conditions.